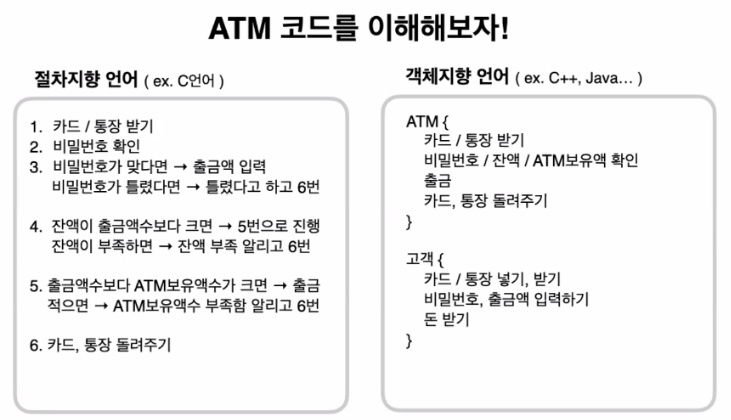
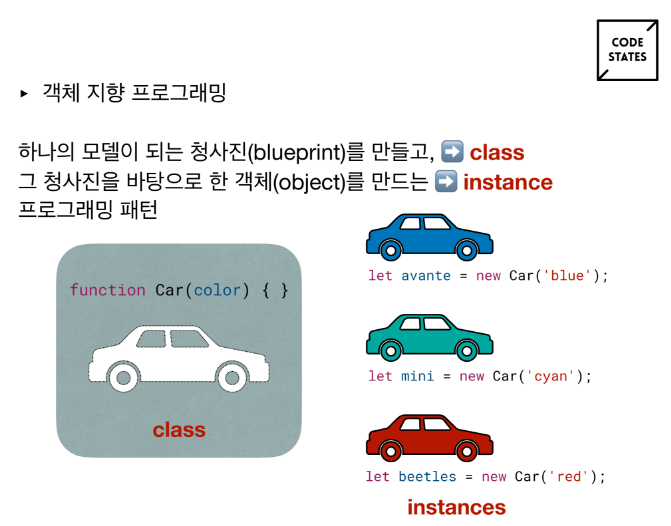
객체지향 프로그래밍에는 9가지 개념들이 있지만,
그 중에 크게 네가지 기본개념이 있다.
1. 캡슐화(Encapsulation)
2. 상속(Inheritance)
3. 추상화 (Abstraction)
4. 다형성 (Polymorphism)
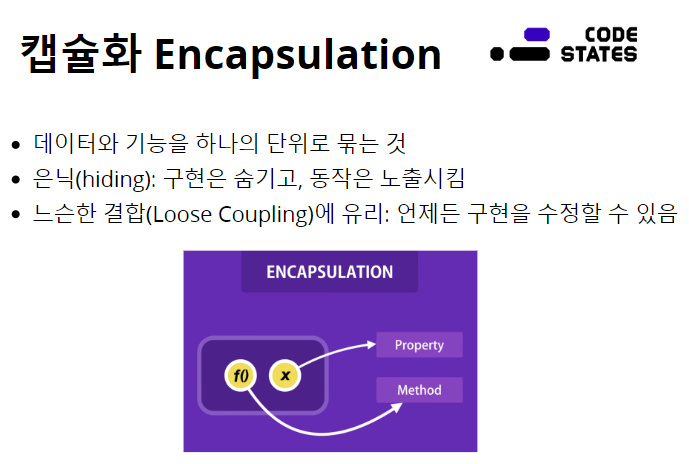
느슨한 결합은
코드 실행 순서에 따라 절차적으로 코드를 작성하는 것이 아니라,
코드가 상징하는 실제 모습과 닮게 코드를 모아 결합하는 것을 의미
캡슐화라는 개념은 "은닉화"의 특징도 포함하고 있는데,
은닉화는 내부 데이터나 내부 구현이 외부로 노출되지 않도록 만드는 것
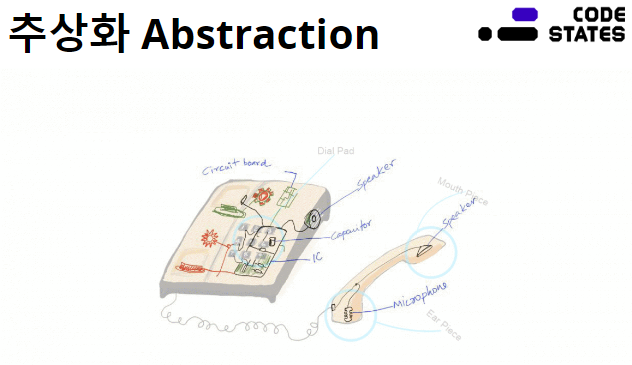
예를들어 전화기로 가정을 들어보자
전화기에는 스피커 기능, 버튼 기능등 여러가지 기능이 탑재되어 있다.
그러나 실제로 우리가 사용할 때에는, 이러한 존재에 대해서는 생각하지 않고 단순히 수화기를 들고
버튼을 눌러서 해결하는 것으로 인터페이스(interface)를 단순화할 수 있다.
추상화는 캡슐화와 비교해서 종종 헷갈려 할 수 있는데
캡슐화가 코드나 데이터의 은닉에 포커스가 맞춰져있다면,
추상화는 클래스를 사용하는 사람이 필요하지 않은 메서드 등을 노출시키지 않고,
단순한 이름으로 정의하는 것에 포커스가 맞춰져 있다.
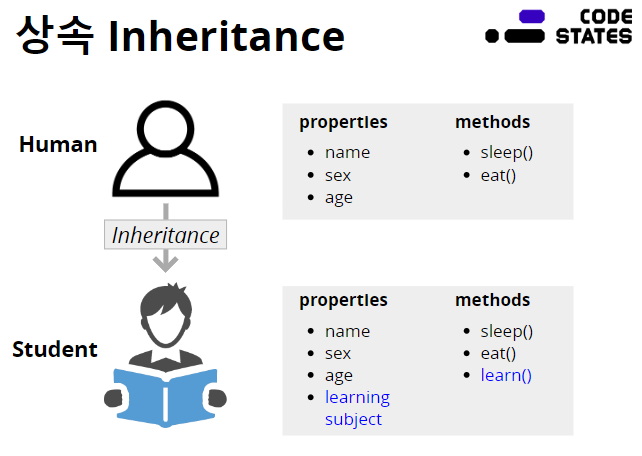
속은 부모 클래스의 특징을 자식 클래스가 물려받는다.
부모/자식으로 이야기하기도 하지만 보다 그 특징을 자세하게 설명하는 용어는
"기본 클래스(base class)의 특징을 파생 클래스(derived class)가 상속받는다"로 표현하는 것이 적합하다.
그러나, 부모/자식이라는 용어를 더욱 많이 사용한다.
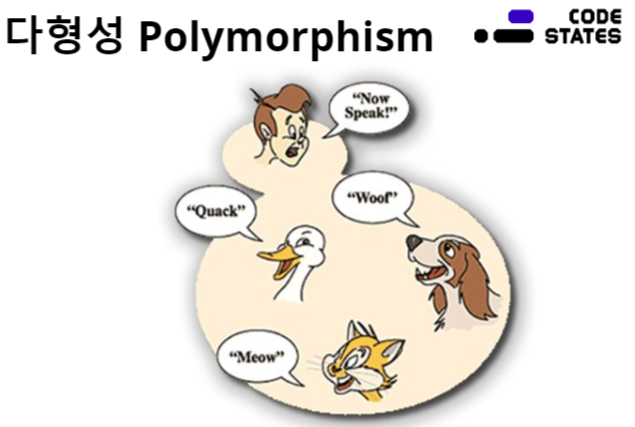
동일한 인터페이스를 사용하여 다양한 객체를 처리할 수 있다.
1. 오버라이딩
하위 클래스에서 상위 클래스의 메서드를 재정의할 수 있고,
동일한 메서드 이름을 사용하면서 다양한 동작을 구현할 수 있다.
2.업캐스팅
하위 클래스의 객체를 상위 클래스의 타입으로 처리할 수 있다.
상위 클래스의 인터페이스에 맞게 다양한 하위 클래스 객체를 사용할 수 있다.
3.동적 바인딩
실행 시간에 객체의 실제 타입에 따라 메서드 호출이 결정된다.
객체의 타입에 따라 적절한 메서드가 호출된다.
'코드스테이츠 프론트과정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [사용자 친화 웹] UI/UX -2 (0) | 2023.06.13 |
|---|---|
| [사용자 친화 웹] UI/UX -1 (2) | 2023.06.13 |
| [클래스와 인스턴스] (0) | 2023.05.11 |
| [DOM 다루기] (0) | 2023.05.09 |
| 코드스테이츠 프론트엔드과정 [JavaScript Koans] (0) | 2023.05.01 |