import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
//sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(a);
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
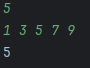
nextInt는 엔터를 버퍼에 남기기 때문에
다음에 s를 입력하기 전에 엔터가 남아있어서
공백이 출련된다.
이것을 수정하기 위해
sc.nextLine()을 사용하면
엔터의 버퍼를 지워주기 때문에
다음 문자를 입력할 수 있다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(a);
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(s);
}
}

숫자만 입력 두번 할 시
nextLine()이 필요없다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
//sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(a);
int s = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(s);
}
}